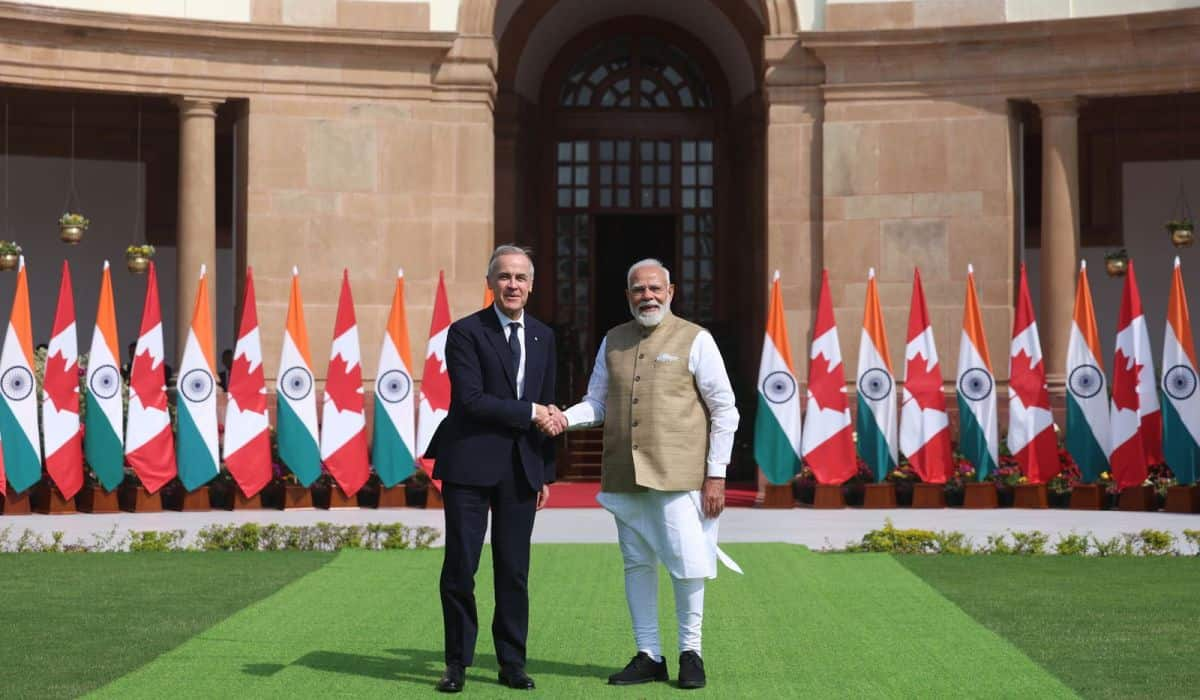
At the invitation of His Excellency Narendra Modi, Prime Minister of India, the Right Honourable Mark Carney, Prime Minister of Canada, paid an official visit to India from February 27 – March 2, 2026. This was Prime Minister Carney’s first visit to India after taking over as the Prime Minister of Canada and is the first bilateral visit to India by a Canadian Prime Minister since 2018. Prime Minister Carney was accompanied by a Canadian high-level delegation that included senior ministers, provincial leaders and leading CEOs.
Commemorating 79 years of establishment of diplomatic relations, the Leaders reaffirmed the importance of the Canada–India relationship, grounded in shared democratic values, deep people-to-people ties, respect for sovereignty and territorial integrity, and a joint commitment to the rule of law.
The Leaders acknowledged that, in an increasingly complex and uncertain global context, a strong, resilient, and forward-looking partnership between two vibrant democracies contributes meaningfully to mutual prosperity and to advancing shared global priorities. They underscored that closer cooperation between India and Canada will help reinforce international rules and norms that are applied fairly, strengthen economic resilience, promote sustainable development, and address global challenges including climate change, rapid technological transformation, and public health. The Leaders affirmed their shared resolve to work together bilaterally and in multilateral fora to uphold democratic values, support inclusive growth, and contribute to peace, stability, and prosperity in the Indo-Pacific and beyond.
Building on this shared vision, the Leaders agreed to adopt the principle of "Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” or "One Earth, One Family, One Future” as the overarching guiding framework for the renewed India–Canada Strategic Partnership, reflecting their commitment to sustainability, inclusivity, and collective global responsibility. They underscored the alignment between India’s vision of Viksit Bharat and Canada’s Build Canada Strong agenda, and affirmed that enhanced bilateral cooperation across growth, innovation, energy transition, food and nutrition security, trusted digital ecosystems, resilient supply chains, skills and talent mobility, and people-centric development will serve as a catalyst for resilient societies, shared prosperity, and a more sustainable future for both countries and the wider world.
Progress and Implementation of the New Roadmap
Both Leaders welcomed the significant progress achieved since their meetings on the margins of the G7 Summit in Kananaskis and the G20 Summit in Johannesburg in the implementation of New Roadmap for Canada–India Relations, thereby providing a clear direction for strengthening the Canada–India partnership. They noted with satisfaction the increased frequency of two-way Ministerial-level engagements, which have injected renewed momentum into bilateral cooperation across priority sectors; welcomed the activation of various institutional dialogue mechanisms and enhanced sub-national engagement, underscoring their importance in deepening mutual understanding and policy coordination; acknowledged the return of diplomatic representatives to their respective missions; and appreciated the constructive steps taken toward the gradual normalization of bilateral ties, reflecting a shared commitment to strengthening bilateral relations in a spirit of mutual respect, accommodation, and cooperation.
The Leaders highlighted the strong commercial foundation underpinning bilateral ties, reflected in the launch of negotiations of a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) and in significant business announcements and investment commitments in recent months. These developments demonstrate the expanding scale, diversification, and sophistication of the bilateral economic relationship and signal growing confidence among businesses and investors in both markets. The Leaders noted that sustained engagement between industry and government, supported by an enabling policy environment, will be essential to unlock new opportunities in priority sectors and to translate commercial momentum into long-term, mutually beneficial economic growth.
Building on this momentum, the Leaders agreed to deepen collaboration across the following priority sectors:
ONE EARTH
Strategic Energy Partnership
Recognizing their complementary strengths as energy powers, the Leaders agreed to advance the India-Canada Strategic Energy Partnership aimed at deepening long-term cooperation across the energy value chain. They reaffirmed the immense importance of energy security and diversification of supply for the safety, wellbeing, and economic vitality of both countries, and underscored their shared commitment to enhancing collaboration across clean energy, conventional energy, civil nuclear energy, and critical minerals to promote affordability, sustainability, and economic growth.
The Leaders welcomed the re-launch of the Canada–India Ministerial Energy Dialogue at India Energy Week 2026 as a key institutional platform to sustain high-level policy dialogue and strengthen strategic cooperation on energy security, diversification of supply, and long-term market integration. They also welcomed the finalization of a Joint Action plan under the Dialogue.
The Leaders also highlighted the potential to broaden cooperation across clean energy and climate-related value chains, including renewable energy, hydrogen and its derivatives, biofuels, sustainable aviation fuel, battery storage, and electricity systems modernization, recognizing the central role of these sectors in advancing shared climate objectives and energy transition goals.
The Leaders underscored solutions for carbon capture, utilisation and storage (CCUS) as a key area of cooperation offering a significant opportunity for the sustainable production of energy and critical minerals.
The Leaders reaffirmed their intention to promote sustained government-to-government and business-to-business engagement, including continued expert collaboration and cooperation through bilateral and multilateral mechanisms, to ensure that the Strategic Energy Partnership delivers tangible, long-term benefits for both countries.
Energy Trade
The leaders noted that strengthened institutional engagement would support expanded bilateral energy trade, including in liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), crude oil, refined petroleum products, potash, and uranium supply offtakes. In this regard, they welcomed the conclusion of a CAD $2.6 billion commercial agreement between Cameco and the Department of Atomic Energy for the long-term supply of uranium, contributing to India’s civil nuclear energy generation, clean energy transition objectives, and long-term energy security.
The Leaders noted that Canada is poised to become a major global supplier of LNG and welcomed India’s intention to source LNG from Canada. They further welcomed the emergence, over the past five years, of Canada as an important supplier of heavy oil. With India, positioned to be the largest contributor to incremental global energy demand growth over the next two decades, beyond its current position as the world’s third-largest oil consumer and fourth-largest LNG importer, both sides acknowledged the significant potential to further expand bilateral energy trade. This includes increased oil and LNG imports by India from Canada, as well as the supply of refined petroleum products from India to Canada. In this context, Canada reaffirmed its plans to expand heavy oil export infrastructure and supplies of LNG to the Indo-Pacific market through Canada’s stated goal of producing 50 million tonnes of LNG per year by 2030 and up to 100 million tonnes by 2040.
The Leaders welcomed discussions between Indian public sector oil and gas companies and Canadian energy firms to expand bilateral cooperation in liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). They noted ongoing engagement aimed at concluding India’s first long-term LPG supply arrangement with Canada and expressed confidence that such partnerships will further diversify energy trade, strengthen supply security, and create new opportunities for collaboration across the hydrocarbon value chain.
Both sides also reaffirmed support for greater private investment flows and long-term offtake arrangements including through tools, such as loans, financing, and equity investments to support commercially viable energy partnerships. Through the India-Canada Energy Dialogue, both sides will set out a joint work plan to explore long-term contracts and address the challenges to growing this trade including shipping costs and increasing availability of Canadian heavy oil supply.
Critical Minerals Cooperation
The Leaders underscored their commitment to deepening long-term, reciprocal investment partnerships across the energy and natural resource sectors, recognizing the scale of ongoing projects and emerging opportunities in both markets. They further welcomed the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding on Critical Minerals Cooperation, reflecting their shared commitment to building resilient, secure, and diversified critical minerals supply chains. In this context, they welcomed India’s endorsement of the G7 Critical Minerals Action Plan, which supports diversified and responsible production and supply of critical minerals and encourages investment and innovation in value chains essential for clean energy, advanced manufacturing, and technology. The Leaders also discussed Indian presence at the Prospectors and Developer’s Association of Canada (PDAC) meeting in March 2026, and commitment for a Ministerial-led Indian energy and industry delegation to Canada in summer 2026 to support robust commercial outcomes for Canadian and Indian companies.
Leaders agreed to strengthen collaboration in investment to support clean energy technologies and future-oriented industries. They agreed to deepen cooperation on critical minerals and energy transition pathways, including exploring collaboration on helping to secure India’s mineral stockpiling initiative, and supporting robust commercial outcomes for Canadian and Indian companies, while also sharing expertise on emissions reductions, and transition technologies.
Clean Energy Cooperation
The Leaders also welcomed the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding on Clean Energy Cooperation, establishing a comprehensive institutional framework to advance bilateral collaboration across solar, wind, bioenergy, small hydro, energy storage, and capacity-building. They agreed to build a mutually beneficial clean energy partnership that strengthens energy security, accelerates the energy transition through information exchange and joint investment opportunities, and promotes two-way public–private engagement across the renewable energy value chain, including through a dedicated Joint Working Group. This cooperation will support sustainable economic growth, regional resilience in the Indo-Pacific, and the shared objective of building an inclusive clean energy future.
Canada expects to double electricity supply by 2050 and significantly expand deployment of renewable energy and energy storage. Concurrently, India has demonstrated leadership and capacity in large-scale solar and grid-level energy storage technologies along with scalable models in rooftop solar and other forms of distributed renewable energy solutions. In this regard, Leaders committed to convening a India-Canada Renewable Energy and Storage Summit in 2026 to bring together industry, investors, and government decision-makers to expand and diversify trade of these technologies into Canada, including through future procurements and supply chain partnerships.
Climate and Environment
They welcomed the deepening of cooperation under the existing Memorandum of Understanding on Climate Change and Environment, underscoring the strength of the partnership. The Leaders reaffirmed their shared commitment to science-based, inclusive, and equitable climate action. They highlighted ongoing bilateral efforts to advance sustainable development by addressing climate change, biodiversity loss, pollution, and ecosystem degradation, and agreed to strengthen collaboration on climate mitigation and adaptation, biodiversity conservation, and reducing plastic pollution, with particular attention to building resilience and supporting vulnerable communities.
Global Clean Energy Platforms
India welcomed Canada’s decision that it intends to pursue membership in the International Solar Alliance, underscoring Canada’s strong commitment to advancing clean energy and climate action. The leaders noted that Canada’s participation will strengthen international cooperation on solar deployment, innovation, and capacity-building, particularly in developing and climate-vulnerable regions. They agreed that enhanced collaboration through the International Solar Alliance will complement bilateral clean energy initiatives and contribute meaningfully to accelerating the global energy transition and achieving shared sustainability goals.
India welcomed Canada’s signing of the foundational documents to upgrade its participation in the Global Biofuels Alliance as a Full Member. This step will further advance the adoption of sustainable biofuels globally and strengthen cooperation across the biofuels supply chains, standards, and deployment, including collaboration on sustainability standards and lifecycle emissions.
Sustainable Agriculture and Nutritional Security
Recognizing the growing complementarity between India and Canada in agriculture and agri-food systems, the Leaders underscored the importance of strengthening cooperation to enhance food security, farm productivity, and resilient supply chains. The Leaders highlighted expanding opportunities for collaboration in agri-technology, research, and value-added food production, and agreed that deeper agricultural partnership will advance sustainable farming practices, nutrition security, and mutually beneficial trade and investment.
The Leaders welcomed the proposal to collaborate on establishing a Canada–India Pulse Protein Centre of Excellence at NIFTEM Kundli. They noted the complementary strengths of the Province of Saskatchewan as a global leader in pulse production and innovation, and India as the world’s largest producer and consumer of pulses. The Leaders agreed that this initiative would strengthen agri-food research collaboration, advance pulse protein processing and fortified food development, and contribute to improving access to affordable, high-quality nutrition, while reinforcing sub-national partnerships and industry–academia linkages between the two countries.
ONE FAMILY
Investing in Talent
The leaders underscored the central role of education and talent mobility in advancing people-to-people ties between India and Canada. They noted that the movement of students, researchers, and professionals has been mutually beneficial, strengthening innovation ecosystems and economic growth in both countries.
Recognizing the importance of international academic collaboration in fostering innovation; improving learning outcomes; and building a future-ready workforce, the Leaders agreed to deepen cooperation between higher education institutions by enhancing industry aligned skills training; expanding joint; dual-degree and twinning programs; facilitating the establishment of offshore campuses of leading Canadian institutions in India; strengthening research partnerships in emerging technologies; and revitalizing the Joint Working Group on Higher Education to further support cooperation in this area.
The Leaders welcomed the Memorandum of Understanding between India’s All India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) and Canada’s MITACS to expand the Globalink Research Internship program, enabling approximately 300 Indian undergraduate students annually to undertake research placements at Canadian universities. They noted that this flagship initiative will strengthen institutional linkages, deepen academic collaboration across disciplines, and build future-ready skills through hands-on research and professional training.
Leaders welcomed a new Joint Talent and Innovation Strategy, a developing initiative aimed at embedding Canadian research and innovation capacity in shared priority sectors and strengthening two-way talent flows through structured mobility, joint training pathways, and research collaboration.
The Leaders underscored the importance of fostering deeper institutional partnerships, researcher mobility, and knowledge exchange to advance innovation, build capacity, and support shared Indo-Pacific priorities. In this context, they welcomed Canada’s Indo-Pacific Scholarships and Fellowships for Canadians (IPSFC) program as a meaningful step toward strengthening academic and research linkages between Canadian and Indian institutions. They noted that over 85 Canadian graduate students and researchers from 11 Canadian post-secondary institutions will travel to India under the program to collaborate with leading Indian academics across priority areas including clean hydrogen, climate resilience, artificial intelligence, trade and supply chain resilience, and sustainable development. The Leaders also welcomed the conclusion of twenty-four education-related MOUs.
People-to-People and Cultural Cooperation
Recognizing the deep historical connections and vibrant people-to-people links between India and Canada, the Leaders underscored that cultural cooperation is a vital pillar of the bilateral relationship. They noted that sustained cultural exchange strengthens mutual understanding, celebrates diversity, and builds lasting connections between societies, while also supporting creative economies and innovation. The Leaders agreed that closer collaboration in culture, heritage, and creative industries will further enrich bilateral ties and contribute meaningfully to inclusive growth and shared prosperity.
The Leaders welcomed the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding on Cultural Cooperation, reaffirming their commitment to deepen people-to-people ties between the two countries through expanded collaboration in the arts, heritage, audiovisual media, music, and creative industries. They agreed to strengthen cooperation between cultural institutions and creators in both countries through targeted initiatives.
The Leaders also underscored the potential of emerging technologies, including virtual and augmented reality and artificial intelligence, for the cultural sector and supporting sustained cultural dialogue, creative partnerships, and mutual understanding in this area.
The Leaders reaffirmed the importance of empowering Indigenous and Tribal communities in both countries and recognized their rich cultural heritage, traditional knowledge systems, and enduring contributions to national development. They welcomed Bharat Tribal Festival (BTF) 2026 as an example of an important platform to promote global exchanges in entrepreneurship, cultural preservation, and sustainable livelihoods. The Leaders agreed to encourage dialogue and collaboration in areas such as cultural exchange, skills development, traditional knowledge, and market access for community-based products, with a view to strengthening inclusive growth and reinforcing people-to-people ties grounded in mutual respect for diverse cultures and traditions.
The Leaders welcomed the recent Canada–India Track II Strategic Dialogue, which brought together policymakers, experts, business leaders, and civil society to explore pathways for translating the diplomatic reset into concrete cooperation across issues such as economic resilience, emerging technologies, energy security, and people-to-people exchanges. They noted that this high-level exchange underscored the importance of institutionalized engagement, expanded sectoral collaboration, and shared policy dialogue as enduring complements to official government-to-government mechanisms. The Leaders agreed that sustained dialogue across formal and Track II platforms will help deepen mutual understanding, strengthen bilateral cooperation, and inform practical, forward-looking initiatives that deliver tangible benefits for both societies.
3The Leaders recognized the strong history of collaboration in the field of civil aviation between the two countries and its significant contribution to economic growth, connectivity and people-to-people exchanges. They expressed their desire to deepen this collaboration through continued work to renew their joint Memorandum of Understanding on Civil Aviation Cooperation to help promote safe, secure, sustainable and resilient aviation ecosystems in both countries.
ONE FUTURE
Science and Technology Architecture
Recognizing that technology and innovation are central drivers of economic growth, competitiveness, and societal resilience, the Leaders underscored the importance of deepening India–Canada cooperation in science, technology and innovation. This convergence highlights the need to revitalize institutional mechanisms that can translate ambition into coordinated, results oriented collaboration. The relaunch of the Joint Science and Technology Cooperation Committee (JSTCC) is a pivotal step providing a renewed platform to enhance cooperation in critical and emerging technologies, strengthening secure and trusted digital ecosystems, accelerating clean tech and energy innovation, and expanding research partnerships.
Space Cooperation
The Leader’s discussed the urgency and mutual benefit of strategic partnership on space cooperation by respective agencies and private sectors. On the basis of trust built between the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) over the 30 years since a Memorandum of Understanding on space cooperation was first signed in 1996, space agencies and their national business and research eco-systems are positioned to rapidly and jointly pursue emerging opportunities.
This partnership will be guided by an ambitious Implementation Arrangement under the MOU to operationalize joint projects and facilitate technical collaboration in new and emerging domains, including atmospheric sciences, space exploration involving space robotics and human spaceflight, and quantum communication technologies, supported by enhanced capacity‑building and knowledge exchange between their agencies. More broadly, they affirmed the importance of strengthening connections across their national space ecosystems, encouraging partnerships among government organizations, industry, startups, academia and research institutions to leverage complementary strengths, drive innovation, and contribute to shared development objectives.
Digital and AI Cooperation
Building upon space cooperation, India and Canada intend to explore joint initiatives to integrate AI into space and aerospace technologies. By co-developing these AI tools for space applications and earth observation, both countries will advance innovation and reinforce their technological sovereignty.
The Leaders agreed to explore collaboration on AI assisted tools to strengthen the diagnostic capabilities of distance medicine to deliver modern, reliable health care to the remote regions of both countries.
Recognising the value of industry and academia partnerships, both sides intend to establish a program of cross-border work-integrated learning opportunities that will enable Indian engineers and researchers to gain hands-on experience at Canada’s world class AI research institutes and Canadian engineers gaining exposure to India’s expertise in the large-scale deployment of digital public infrastructure ecosystem.
Recognizing the growing importance of resilient electric grid systems in the context of rising energy demand and the expanding role of renewable energy, both sides agreed to strengthen cooperation through knowledge-sharing on the development of AI algorithms to predict energy surges and to better manage battery storage across different climatic conditions to support reliable, efficient and climate-resilient power systems in both countries.
The Leaders welcomed progress under the Australia–Canada–India Technology and Innovation (ACITI) Partnership and noted the recent meeting of the AI Ministers of the three countries on the margins of the AI Summit in New Delhi. They agreed to develop a joint workplan to advance practical trilateral cooperation in artificial intelligence and digital technologies and underscored the potential for deeper collaboration across digital infrastructure, semiconductor and electronics manufacturing, high-performance computing, Internet-of-Things (IoT), cybersecurity, and startup ecosystems. The Leaders further agreed to strengthen policy and regulatory exchanges to advance AI sovereignty, inclusivity, access and trustworthiness; promote AI adoption and related business-to-business partnerships; and advance joint capacity-building through skills development, training, and knowledge-sharing, with a view to fostering trusted innovation ecosystems and delivering tangible outcomes. The Leaders welcomed the codification of this work through the signing of a trilateral Australia-Canada-India MOU on Cooperation in Technology and Innovation.
To translate this shared vision into concrete outcomes, the Leaders agreed to structure the renewed India–Canada Strategic Partnership around two foundational layers.
Foundational Layer – 1: Security and Defence Cooperation
Security Cooperation
The Leaders welcomed the progress made under the regular bilateral security dialogue convened at the level of the National Security Advisors and the agreement to a shared workplan to guide enhanced cooperation on national security and law enforcement priorities. As pluralistic democracies, they agreed to deepen collaboration to address issues relating to violent extremism, terrorism, organized crime, including the illegal flow of narcotics and fentanyl precursors, cybercrime, extortion, financial fraud, trafficking and related criminal networks. The Leaders supported the establishment of security and law-enforcement liaison mechanisms to streamline bilateral communication and enable timely information-sharing and committed to strengthening cooperation on cybersecurity and immigration enforcement, consistent with domestic laws and international obligations. They also called for the early convening of the next meeting of the Joint Working Group on Counterterrorism.
Defence Cooperation
The Leaders recognize the value of expanding practical military cooperation and welcome opportunities to deepen defence relations through cooperative activities, joint training opportunities, and professional military exchanges. Leaders welcomed a new Maritime Security Partnership in areas such as Defence Material Cooperation, Supply Chain Resilience, and Training and Exercises.
Both countries agree to institutionalizing an India–Canada Defence Dialogue which will exchange views on respective defence policies, regional and global security developments, and strategic outlooks in order to identify opportunities for greater defence collaboration.
In this context, they welcomed Canada’s appointment of a Defence Attaché to India and India’s concurrent accreditation of its Defence Attaché in Washington D.C. to Canada as important steps toward strengthening institutional linkages.
Multilateral and Indo-Pacific Engagement
Both countries agreed to deepen cooperation in a range of regional and global fora. These engagements will strengthen coordination and promote a shared understanding of priorities in an increasingly complex strategic environment.
The Leaders agreed that the Indo-Pacific represents a region of growing strategic and economic importance and reaffirmed their shared commitment to a free, open, inclusive, and resilient Indo-Pacific. They underscored the value of practical cooperation in promoting sustainable development, maritime safety and security, climate resilience, connectivity, and capacity-building across the region. The Leaders committed to strengthening coordination through regional and global institutions and partnerships, leveraging complementary strengths to support infrastructure development, digital inclusion, disaster preparedness, and people-centric growth, while advancing a rules-based international order that respects sovereignty and territorial integrity.
The Leaders noted the growing convergence between India’s vision for the Indian Ocean Region and Canada’s Indo-Pacific Strategy, grounded in shared interests in stability, sustainable development, connectivity, and inclusive growth. India welcomed Canada’s interest in joining the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA) as a Dialogue Partner, recognizing the value Canada can bring through its expertise in maritime governance, climate resilience, blue economy, and capacity-building. The Leaders agreed to strengthen cooperation in the Indian Ocean through practical initiatives supporting disaster preparedness, infrastructure development, digital inclusion, and people-centric growth, and affirmed their commitment to working together with regional partners to advance a free, open, inclusive, and resilient Indo-Pacific.
Foundational Layer – 2: Advancing Trade Partnership
Ministerial Dialogue on Trade and Investment
The Leaders noted that the renewed Ministerial Dialogue on Trade and Investment marked a renewed phase of engagement aimed at reinvigorating bilateral trade and investment ties and setting a forward-looking agenda for cooperation, anchored in shared democratic values and growing economic complementarities.
CEPA and Trade Architecture
The Leaders reaffirmed their shared commitment to strengthening bilateral economic engagement through the resumption of discussions toward an ambitious and mutually beneficial Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA). The Leaders expressed confidence that a comprehensive trade framework would serve as a durable economic anchor for the partnership and support the shared aspiration of expanding bilateral trade to CAD 70 billion / INR 4.65 lakh crore by 2030. They welcomed the finalization and signing of the Terms of Reference for CEPA negotiations and the launch of formal negotiations and expressed their shared commitment to conclude the talks by end-2026.
Commercial Momentum
Acknowledging the evolving global economic landscape, both sides underscored the importance of a resilient, reliable, and predictable trading relationship that enhances supply chain stability, mitigates external vulnerabilities, accommodates each other’s sensitivities, and promotes mutually beneficial cooperation across priority sectors. They further recognized the deepening integration of their economies, reflected in the substantial workforce employed by Canadian companies operating in India and by Indian companies operating in Canada, demonstrating a significant two-way commercial presence that already anchors the partnership.
To impart greater commercial momentum to bilateral trade and investment ties, the Leaders welcomed a program of four reciprocal Ministerial-led trade and investment engagements, including two visits to Canada and two visits to India, accompanied by business delegations. They noted that these exchanges will help unlock new commercial opportunities, deepen private-sector partnerships, and further integrate the economies of both countries.
India-Canada CEO Forum
The Leaders welcomed the reconstitution of the India–Canada CEO Forum as a key platform to deepen private-sector engagement and advance practical cooperation across priority sectors. They encouraged business leaders from both countries to leverage the Forum to identify new opportunities in trade, investment, innovation, and supply chain resilience, and to provide actionable recommendations to support CEPA negotiations and broader economic objectives. The Leaders agreed that stronger collaboration between industry, government, and financial institutions will be essential to taking bilateral economic cooperation to the next level and delivering tangible benefits for businesses and citizens in both countries.
Finance Ministers Economic Dialogue
The Leaders welcomed the launch of the Finance Ministers’ Economic and Financial Dialogue that will bring together finance officials on issues such as payments modernization, financial stability, fintech innovation and capital markets development. As an early priority, this will include collaboration on the future of instant payments and explore opportunities on cross-border remittances and merchant payments. The National Payments Corporation of India and Payments Canada would be invited to participate, with the aim of boosting bilateral trade, while supporting tourism, education, remittances, and growth for SMEs in both countries. They noted that the inaugural Finance Ministers Economic Dialogue will be hosted at a mutually agreed time in 2026.
Conclusion
Prime Minister Carney expressed his sincere appreciation to the Government and people of India for their warm hospitality and reaffirmed Canada’s strong commitment to advancing this comprehensive partnership.
Both Leaders welcomed continued high-level engagement and expressed confidence that the initiatives outlined in this Joint Statement will further deepen the India–Canada partnership, strengthen mutual trust, and deliver tangible, long-term benefits for both countries and their peoples.
They affirmed that a stronger India–Canada partnership will also contribute positively to regional stability, global resilience, and shared prosperity, reflecting their common commitment to building a more inclusive, sustainable, and secure future.