For decades, Uttar Pradesh languished in neglect, with development disproportionately focused on select regions, leaving the state's vast population marginalized and deprived. The approach driven by political agendas perpetuated poverty and societal divisions and hindered the nation's and the state's progress. However, a transformative shift occurred in 2014 when Prime Minister Narendra Modi's government ushered in a new era of rapid development for the state. Recognizing Uttar Pradesh's pivotal role in realizing Bharat's full potential by 2047, the government mobilized every available resource, from agriculture to industry, to drive the state's growth.
One of the key focus areas has been infrastructure development, with significant improvements seen in roadways, railways, airways, and waterways. Over 2,450 kilometres of new railway lines have been commissioned in UP since 2014. About 4,000 km of national highways have been constructed in UP in the last five years. The government's commitment to modernizing railway infrastructure is also evident in the ambitious Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) corridor, which spans 82.15 km.
Air connectivity has also received a significant boost, with the UDAN scheme facilitating flight operations from six airports in UP, including Agra, Prayagraj, Bareilly, Kanpur, Hindon, and Kushinagar, over the last five years. Recently, PM Modi inaugurated the Maharshi Valmiki International Airport in Ayodhya. Moreover, UP is set to welcome five additional airports soon, with an International airport in Jewar expected to be operational by the end of 2024.
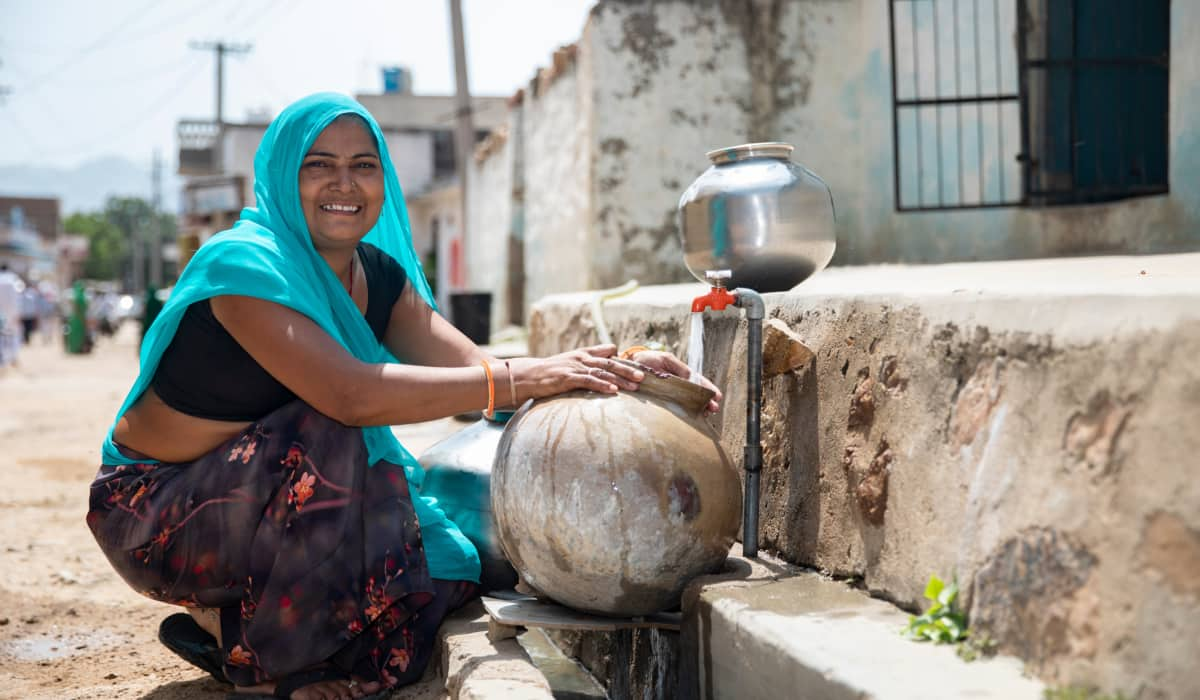
Public welfare has remained a top priority, with significant strides in housing, electrification, and water supply. Over 35 lakh houses have been completed under the PM Awas Yojna, while the Saubhagya Scheme has electrified over 91.8 lakh households. The Jal Jeevan Mission has also provided tap water connections to 1.35 crore households. Welfare schemes like the Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan have offered financial security to over 6.68 lakh unorganized sector workers. UP registering the most significant decline in poverty, with 5.94 crore people emerging from multidimensional poverty in the last nine years, reflects welfare schemes' efficacy in uplifting the marginalized sections of society.
Significant strides have been made in the healthcare sector, with the establishment of two AIIMS institutes in Raebareli and Gorakhpur and the distribution over 4.95 crore Ayushman health cards in UP. Approval has also been granted for 27 new medical colleges in the state, while 11 Government Medical Colleges have been upgraded with Super Specialty Blocks (SSBs).
The state's progress in women's empowerment has been equally noteworthy, with initiatives to enhance economic participation and social inclusion for women. Over 72.65 lakh women have been mobilized into self-help groups, empowering them economically and socially. Additionally, over 1.83 lakh women-owned MSMEs have been registered on the Udyam
Registration Portal, reflecting their growing role in entrepreneurship.
Education and skill development have been prioritized to harness the potential of the youth, with over 39.5 lakh candidates trained under Skill India. Job fairs across the state have facilitated employment opportunities, with 4.26 lakh jobs provided to job seekers since 2020-21.
Moreover, entrepreneurship has been encouraged through schemes like Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana, leading to the extension of over 3.8 crore loans to aspiring entrepreneurs. The government's support for startups has resulted in around 10,000 entities being recognized.
Furthermore, the state has made significant progress in the Ease of Doing Business Rankings, now holding the second position nationwide. Uttar Pradesh now serves as a crucial hub for the Eastern and Western Dedicated Freight Corridors and two major Defence Industrial Corridors within the country, one of which is in Uttar Pradesh. Additionally, initiatives like PM Mitra Park in Lucknow and Hardoi are expected to create numerous employment opportunities in the state.
Agricultural development initiatives in Uttar Pradesh have prioritized enhancing productivity and sustainability. Under PM-KISAN, over Rs. 64,330 crore has been disbursed to over 2.62 crore beneficiaries in UP. At the same time, the Pradhan Mantri Kisan MaanDhan Yojana (PM-KMY) has seen enrolment of 2.52 lakh farmers from UP. Implementing the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY) has provided insurance coverage to 3.6 crore farmer applications in UP since 2016-17, with Rs. 4,830 crore disbursed as claims. Furthermore, UP has seen the registration of 1181 Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs) and the coverage of 4.26 lakh hectares under Micro Irrigation through the Per Drop More Crop scheme from 2015-16 to 2022-23, leading to the efficient utilization of water resources and a significant increase in agricultural yield.
The state has also focused on developing tourism, with projects approved under the Swadesh Darshan and PRASAD Scheme to enhance key destinations such as Varanasi, Ayodhya, Mathura-Vrindavan, and the banks of the holy Ganges.
In conclusion, the progress made by Uttar Pradesh under Prime Minister Narendra Modi's leadership demonstrates the transformative power of visionary governance and inclusive development. With sustained momentum and collective resolve, Uttar Pradesh is poised to emerge as an inclusive and sustainable development model, contributing significantly to Bharat's journey towards becoming a global economic powerhouse.