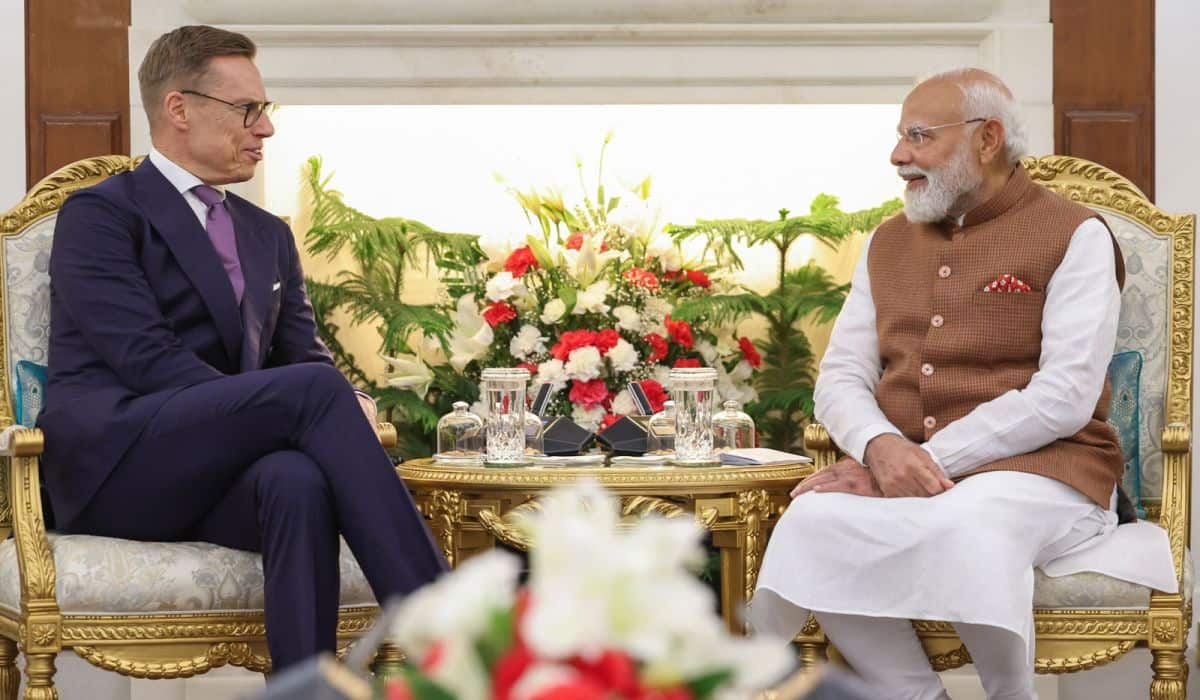
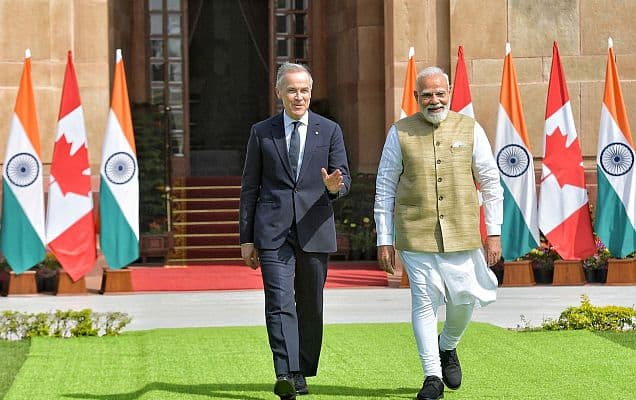
At the invitation of the Hon'ble Prime Minister of India, Shri Narendra Modi, President of the Republic of Finland, H.E. Dr. Alexander Stubb, is on a State Visit to India from 4-7 March 2026. President Stubb, who is on his first visit to India in his present capacity, is visiting New Delhi and Mumbai and is accompanied by Ms. Sari Multala, Minister of Climate and the Environment of Finland, Mr. Matias Marttinen, Minister of Employment of Finland, and a high-level delegation comprising of officials and business leaders. Prime Minister Modi inaugurated the 11th edition of the Raisina Dialogue on 5 March 2026 in New Delhi with President Stubb as the Chief Guest delivering the Inaugural Keynote Address. President Stubb’s visit follows the visit of H.E. Mr. Petteri Orpo, Prime Minister of the Republic of Finland for the AI Impact Summit in February 2026.
On 5 March 2026, President Stubb was warmly welcomed by Hon’ble President of India Smt. Droupadi Murmu at Rashtrapati Bhavan. Prime Minister Modi and President Stubb held wide-ranging discussions during a bilateral meeting, and jointly addressed the media. Prime Minister Modi also hosted a luncheon in honour of the visiting dignitary.
The President of Finland congratulated India for successfully hosting the AI Impact Summit 2026. Both Leaders shared the view that working towards safe, trustworthy, and inclusive development of AI is of paramount importance.
The Leaders affirmed the deep and enduring friendship between India and Finland, built on a foundation of mutual respect and the values of democracy and rule of law, as well as commitment to global peace, security, and international law.
The Prime Minister of India and the President of Finland reiterated their commitment to the rules-based international order and multilateral cooperation, with the UN at its core.
The Leaders underlined the importance of redoubling efforts to reach the Sustainable Development Goals, and the importance of global cooperation against the challenges of climate change and loss of biodiversity.
Welcoming the landmark Free Trade Agreement between India and the European Union concluded in the India-EU Summit on 27 January 2026, the Leaders acknowledged the immense and mutually beneficial opportunities for both parties of increased trade and investments, including for the India-Finland bilateral relationship.
Building on the momentum provided by the India-Finland Virtual Summit on 16 March 2021 and the meetings of the Prime Ministers of both countries in the margins of two editions of India-Nordic Summit in 2018 and 2022 in Stockholm and Copenhagen respectively, as well as during the AI Impact Summit in February 2026, the Leaders emphasized their shared commitment to continue expanding and deepening the cooperation between the two nations. In this spirit, the leaders agreed to elevate the India-Finland relations to a Strategic Partnership in Digitalization and Sustainability, based on converging interests and mutual benefits.
Trade and Investment
The Prime Minister of India and the President of Finland called upon the business community to make use of the vast opportunities unleashed by the landmark India-EU FTA. In this context, The Leaders agreed that the aim should be to double the value of current trade between India and Finland by 2030.
The Leaders took note of the lively interactions between the respective business communities, reflected by the large business delegation visiting India together with the Finnish President, as well as the companies that joined the Finnish Prime Minister in February in connection with the AI Impact Summit in New Delhi. Both leaders expressed confidence that the India-Finland Business Summit and CEOs interaction scheduled to take place in Mumbai on 7 March would help pave the way for enhancing trade, technology collaboration and investments ties.
The Leaders welcomed the growing startup collaboration, manifested by the active participation of innovative Indian startups in Slush in Helsinki and Finnish startups in Startup Mahakumbh in New Delhi, as well as initiatives such as the Indo-Finland Startup Corridor.
Digitalization
Recognizing the transformative power of digitalization as a key driver of inclusive social and economic development, the Leaders identified digital transformation, including new and emerging technologies such as 5G, 6G, high-performance and quantum computing and Artificial Intelligence, as priority areas where collaboration based on mutual trust and benefit can be strengthened. The Leaders noted India’s experience in Digital Public Infrastructure, including digital payments such as the Unified Payments Interface (UPI), and discussed possibilities for cooperation in this area.
Against this backdrop, the Leaders asked the relevant ministries to establish a cross-sectoral Joint Working Group on Digitalization to define priorities and foster work on concrete and substantial actions driving the digital transition.
The Finnish President emphasized the positive impact of the considerable number of Indian professionals in the Finnish R&D and tech innovation ecosystems, contributing to social and economic development by means of digital transition and sustainability for the benefit of all.
The Leaders noted with satisfaction the Joint Calls by the Indian Department of Science and Technology and Business Finland to provide RDI funding for joint initiatives of Indian and Finnish companies and research organizations with focus on semiconductors, 6G, and energy systems. They also took note of the cooperation framework between Bharat 6G Alliance and the University of Oulu, Finland, welcoming all efforts to further strengthen bilateral collaboration on 6G.
Furthermore, the Leaders welcomed the work between the Indian Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology and Business Finland to further explore avenues of RDI collaboration with special focus on AI, noting also the discussions between the Indian Centre for Development of Advanced Computing and the Finnish IT Centre for Science with respect to High-Performance Computing.
In the field of advanced technology, the Leaders also highlighted Space tech as an emerging area of collaboration with considerable future potential and active private sector engagement between Indian and Finnish players.
Sustainability
On sustainability, both Leaders underlined the great potential in advancing clean energy solutions, notably in areas such as low carbon transition, energy efficiency, biofuels, smart grids, and green hydrogen. In addition, they highlighted the importance of cooperation in circular economy, sustainable water management and meteorology.
To this end, the Leaders welcomed the establishment of a Joint Working Group on Sustainability, bringing together relevant actors from both countries to enhance collaboration on sustainability-related issues.
Moreover, the Leaders underscored the importance of implementing the Memorandum of Understanding on Cooperation in the field of Renewable Energy, encompassing many key areas of collaboration that contribute to sustainability, including bioenergy and waste-to-energy solutions, power storage and flexible RE systems, green hydrogen, as well as wind, solar and small hydro power.
They acknowledged the renewal of the Memorandum of Understanding on Environmental Cooperation, and collaboration under the Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT) and encouraged the parties to advance the deeper collaboration in circular economy, climate action, and sustainability.
Both sides acknowledged that the rapid deployment of Smart Energy solutions, including Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) and other digital grid technologies, has enhanced efficiency while increasing cybersecurity risks to critical power infrastructure. They agreed to explore future areas of cooperation in promoting resilient, reliable and sustainable smart grid systems.
The Finnish President extended his appreciation to India for hosting the next World Circular Economy Forum in the later part of 2026, a Finnish initiative providing a platform to enhance circular economy solutions and bring together leading expertise in the search for new collaborative initiatives.
The Prime Minister of India acknowledged Finland’s active role in bringing together Indian, Finnish and other Nordic stakeholders in the framework of the Indo-Nordic Water Forum, promoting new collaborations and best practices in water resources management and wastewater management for circular economy solutions.
With respect to meteorological collaboration, the Leaders underscored the ongoing cooperation in aerosol monitoring and air quality forecasting between the Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI) and the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD). They welcomed the work to establish a Virtual Research Center between FMI and the Indian Institute of Technology Madras (IITM), also taking note of the already ongoing FMI-IITM research collaboration with multilateral projects exceeding a total value of Euros 11 million.
The Leaders also took note of the exchange of experiences between the Indian Ministry of Rural Development and the National Land Survey of Finland and the Finnish Environment Institute, cities, and companies about Land Stack, an integrated GIS based digital platform of land and property information.
The Leaders welcomed the signing of Memorandum of Understanding on fostering cooperation in the field of Official Statistics which provides a framework for exchange of best practices, methodologies, and technical expertise in the area of official statistics.
Mobility, education, and people-to-people contacts
The Prime Minister of India and the President of Finland recognized the importance of people-to-people contacts in all fields, including skilled workers, specialists and young professionals, researchers and students, businesspersons, and academics, thereby nurturing economic prosperity, contributing to a rich social fabric, and enhancing mutual understanding.
In this context, the Leaders hailed the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding on Migration and Mobility Partnership, laying the frameworks for smooth, orderly, and mutually beneficial mobility for the years to come. Both sides agreed to take the steps required for the implementation of the MoU in a comprehensive and coordinated manner, that serves both India’s and Finland’s prosperity and economic growth. The Leaders also acknowledged the contacts between the respective Foreign Ministries, looking into possibilities of establishing bilateral dialogue on consular matters.
The Leaders took note of the Joint Statement endorsed by the High-Level Dialogue on Cooperation in Education (31 January 2024) and encouraged the relevant parties to accelerate their joint efforts to advance the common agenda, focusing on the agreed areas of secondary education, higher education, skill development, and student mobility.
In this context, they noted the growing interest in India towards the Finnish education system, the increasing cooperation in teacher training, as well as early childhood education institutions and schools that are being set up according to the Finnish model, as concrete expressions of the stakeholders’ shared will and commitment to continue developing the collaboration on education.
Furthermore, the Leaders highlighted the discussions on a bilateral audiovisual co-production agreement that will provide a solid frame to enhance cooperation in the film and gaming industries.
India-EU-relations
Both Leaders welcomed the new Joint India-EU Comprehensive Strategic Agenda, endorsed in the India-EU Summit on 27 January 2026, based on shared values and principles, mutual trust, converging interests, and shared political will. They agreed that India and the EU can be stable, predictable, and trusted partners, building a multifaceted and deepening long-term relationship with many positive outcomes for both sides.
The Leaders underlined that the conclusion of Free Trade Agreement takes the India-EU relations to a new level. In addition to clear economic benefits by enhancing market access and removing trade barriers, both Leaders noted that the FTA could support economic security and resilience through diversifying critical value chains and opening new markets.
As a platform to address key trade, technology, and economic security issues, the Leaders reaffirmed their support to further enhance the work of the India-EU Trade and Technology Council as the cornerstone of the India-EU technology partnership.
The Prime Minister of India and the President of Finland underscored that the signing of India-EU Security and Defense Partnership added another meaningful dimension to the India-EU Strategic Partnership that will deepen co-operation in areas of shared interests, including maritime security, defense industry, cyber and hybrid threats, space, as well as counter-terrorism.
The leaders lauded the signing of the MoU on Comprehensive Framework of Cooperation on Mobility and the launch of pilot European Union Legal Gateway Office in India.
Multilateral cooperation
The Leaders recognized the need to reform the UN system. In this context, they emphasized the importance of a comprehensive reform of the UN Security Council to make it more efficient, representative, inclusive, and reflective of contemporary geopolitical realities. The President of Finland reiterated Finland’s support for the permanent membership of India in a reformed UNSC.
The leaders underscored the vital role of cooperation within the United Nations and other international bodies to safeguard multilateralism and uphold a rules-based international order, including supporting mutual candidacies and nominations.
Both sides agreed to continue their constructive cooperation in multilateral fora, including on peace and security, human rights, sustainable development as well as climate change and biodiversity.
The Leaders reiterated their shared commitment to promoting a free, open, peaceful and prosperous Indo‑Pacific, in accordance with international law, including the UNCLOS. In this context, India welcomed Finland to join the Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative.
Both leaders reaffirmed their commitment to further strengthening cooperation and dialogue on Arctic matters, including through joint research initiatives, academic exchanges, and capacity-building programmes. They took note of the first India–Finland Arctic Dialogue titled "The Himalayan and Arctic Ecosystems: India–Finland Partnership for a Sustainable Future” held in January 2026 in Rovaniemi, Finland, which brought together parliamentarians, government officials, academics and experts to deliberate on strategies and pathways for deepening collaboration on Arctic matters. Both leaders also underscored the importance of advancing cooperation in the structures of the Arctic Council, and within the broader framework of the India-Nordic Summit.
Both leaders unequivocally and strongly condemned terrorism and violent extremism in all its forms and manifestations, including cross-border terrorism. They called for decisive and concerted international efforts to combat terrorism in a comprehensive and sustained manner and in accordance with international law. They agreed to enhance cooperation to counter violent radicalization and extremism, combat financing of terrorism, promote internationally agreed anti‑money laundering standards, prevent exploitation of new and emerging technologies for terrorist purposes, and tackle terrorist recruitment. The leaders reaffirmed strong commitment to continue taking active measures to disrupt the terror financing channels including at the UN and FATF. They condemned in the strongest terms the terrorist attack in Pahalgam, Jammu and Kashmir on 22 April 2025 and the terror incident near Red Fort, New Delhi on 10 November 2025.
Both Leaders agreed to continue to support efforts towards the achievement of a comprehensive, just, and lasting peace in Ukraine through dialogue and diplomacy, based on the principles of the UN Charter and international law, including independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity.
Conclusion
To take forward the cooperation under the India-Finland Strategic Partnership in Digitalization and Sustainability, the Leaders asked the respective Working Groups on Digitalization and Sustainability to develop a future-oriented and concrete Action Plan, including definition of priority areas and related actions, and report back to the Ministry for Foreign Affairs of the Republic of Finland and the Ministry of External Affairs of the Republic of India on the progress achieved.
The President of Finland thanked the Prime Minister of India for the excellent arrangements during his state visit, and both Leaders expressed their appreciation of the open and constructive dialogue, and the forward-reaching and evolving cooperation. They agreed to continue their interaction with a solid foundation in a shared spirit of mutual respect and collaboration. President Stubb invited Prime Minister Modi to pay a visit to Finland, and Prime Minister Modi accepted the invitation.